How To Open Trading Account?
Most often, stock broking firms have thousands of clients. It is not feasible to take physical orders from every client on time. So, to make this process seamless, you open a trading account. Using this account, you can place buy or sell orders online or by phone, which will automatically be directed to the exchange through the stockbroker.
Key Highlights
-
A trading account is crucial for participating in financial markets. It allows individuals and businesses to buy, sell, and manage securities.
-
It acts as an interface between the investor and the Demat account and facilitates the execution of buy and sell orders.
-
Features of a trading account include access to online trading, real-time market information, research and analysis tools, order execution, and margin trading.
What is a Trading Account?
A trading account is an investment account that facilitates placing buy and sell orders. A Demat account keeps many different types of securities that an investor has purchased. However, you need a trading account to buy/sell these securities. It serves as an interface between the investor and the Demat account. A trading account makes purchasing or selling securities in the share market possible.
You need to place an order from your trading account. The stock exchanges will receive your request to purchase or sell a particular security. If you purchase a security, you will receive it in your Demat account after completing the transaction. The required amount shall be deducted from the linked bank account. If you sell a security, it will be debited from your Demat account. You will receive the due funds in the linked bank account.
Features of Trading Account
The following are the key features of a trading account.
-
Access to online trading: You get access to an online portal or mobile app. It makes it easy for account holders to place buy and sell orders as a trading platform's offering. It has research, analysis and real-time market data capabilities.
-
Market Information: To help traders make appropriate decisions, trading accounts include real-time market data, such as stock prices, charts, market news, and more.
-
Research and Analysis Tools: To assist investors in making the right trades, a lot of trading accounts include access to financial news, technical analysis, and research tools.
-
Execution: The trading account carries out the trader's order execution once the trader places it. It finds a suitable match for buy and sell orders and validates the transactions.
-
Margin Trading: Investors can borrow money from their broker to execute transactions through certain trading accounts. For this, they can pledge their securities and use them as collateral.
-
Order Types: Provides investors with various order types, including market, limit, stop-loss, etc, to purchase or sell securities.
Steps To Open A Trading Account?
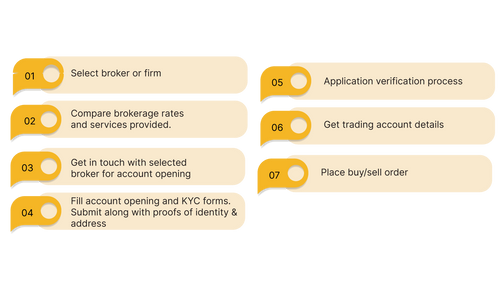
Step 1: Selecting The Right Stockbroker
Choosing the right stock broker for your trading is the first step to open a trading account. Make sure you opt for a reputed broker. It should provide top-notch services to trade in the share market efficiently. Remember, even a few minutes delay in executing transactions may lead to price variation of assets.
Step 2: Compare The Brokerage Rates
Brokerage rates significantly affect the cost overall of trading. Hence, it is crucial to compare the brokerage rates of various brokers. Every broker levies a specific fee for processing your orders. However, charges may vary from broker to broker.
Step 3: Explore different brokerage plans
Some brokers give discounts based on the number of transactions. Such brokerage plans can save you money if your trading volume is high. Further, you can even pay the brokerage in advance to avoid more fees. Here, you can explore Kotak Securities advanced brokerage.
Step 4: Get In Touch With The Selected Brokerage Firm
Next, inquire about the trading account opening procedure with your broker. Some firms also send a representative to your house with the account opening form and the Know Your Client (KYC) form.
Step 5: Fill out the account opening details and do the e-KYC
Fill out the account opening and KYC form. Make sure to submit documents that serve as your identity proof.
Step 6: Complete the verification process
During the verification process, you'll be asked to provide your details in person or over the phone. Provide the relevant information. The broker shall assess your application based on the details you will received the welcome letter from your stock broker.
Step 7: Receive the login credentials
After successful verification, you will receive the login credentials of your trading accounts.You can now access your account and start trading.
Document Required To Open Trading Account
Just like the procedure for opening a demat account, you need to submit proof of identity and address, a passport-size photograph, and the account opening form for opening a trading account. Here is a broad list of documents that can be used as proofs:
-
Proof Of Identity
PAN card, Aadhaar card, voter's ID, passport, driver's licence, bank attestation, IT returns, electricity bill, telephone bill, ID cards with applicant's photo issued by the central or state government.
-
Proof Of Address
Ration card, passport, voter ID card, driving licence, bank passbook or bank statement, verified copies of electricity bills, residence telephone bills, leave and licence agreement or agreement for sale, self-declaration by High Court or Supreme Court judges.
Trading Account Charges
Stockbrokers often charge different trading fees for different kinds of transactions. Trading account charges are one of the primary sources of revenue for brokers. Here are the various trading account charges that investors like you will have to pay.
-
Trading account processing charges: An account processing charge is a nominal fee for processing your account opening application. However, only a few stockbrokers levy these charges on trading accounts.
-
Account opening charges: Stockbrokers charge a one-time account opening fee when opening your trading account. The fee usually varies with different brokers. However, some stockbrokers may not levy it.
-
Fund transfer charges: To trade securities via the stock exchanges, you must first add funds to your trading account. Brokers charge you a nominal fee whenever you transfer funds from your bank account to your trading account. The broker levies these fees to offset the fund transfer payment gateway costs.
-
Brokerage Charges: Brokerage is one of the critical charges associated with a trading account. Stockbrokers charge brokerage for the transactions you make and the services they provide. The fee varies depending on the stockbroker. It may be charged as a flat rate per transaction or as a percentage of the total transaction value.
-
Securities transaction tax (STT): Stockbrokers do not charge STT as part of their trading account charges. Instead, it is a tax that every trader and investor must pay to the government on their purchases and sales of securities.
-
Transaction Charges: The broker charges you a transaction charge every time you trade. Even though stockbrokers levy these charges, they are paid to stock exchanges where the trade was executed.
-
Auto square-off charges: In the case of intraday trades, you must close out all open positions by 3:20 PM (IST). Stockbrokers automatically square off open positions if they remain open beyond the stipulated time. However, brokers generally charge a nominal fee for activating their auto square-off mechanisms. Auto square-off fees usually range from Rs.40 to Rs.60 per transaction.
-
Off-Market transfer charges: In an off-market transfer, securities are transferred from one Demat account to another without involving the stock exchange. The stockbroker charges a nominal fee for such transactions.
Conclusion
Opening a trading account is crucial to start trading in the share market. A trusted stockbroker, low brokerage rates, and different brokerage plans offer a seamless trading experience. Select a broker to open a trading account and fill out the account opening form. Provide the relevant information along with the necessary documents. Once the broker verifies the details, you’ll receive the login credentials. Remember, you must know the various charges associated with a trading account. These include processing fees, maintenance charges, and brokerage fees. Understanding these charges enables investors to choose the right platform and optimise their investment journey.
FAQs on Opening Trading Account
How to open an online trading account in the stock market?
This is how you open an online trading account in the stock market:
- Pick an online brokerage platform that suits your preferences and needs.
- Register by providing your personal information, financial information, and identification documents.
- Fund your account with the required minimum deposit and start trading stocks and other securities online.
What is the best place to open a trading account?
Any SEBI or Exchange-registered entity is the best place to open a trading account. This can be a bank or a stockbroker. The account opening process can be completed online within minutes by filling out a form.
What is the difference between trading and a demat account?
A trading account allows you to execute buy and sell orders for various financial instruments. In contrast, demat accounts hold securities like stocks in electronic form, eliminating the need for physical certificates. These accounts make participating in the stock market easier by making transactions easy and storing investments safely.
A PAN card is a mandatory requirement to initiate the opening of a trading account. Additionally, you'll need to provide proof of identity, which can be fulfilled by documents like a PAN Card (mandatory), Passport, or Driving License. Furthermore, including bank details such as a cancelled cheque or a bank statement containing the IFSC code and account number is essential for the process.
To find your trading account number, log into your online trading account, go to the account dashboard, and find the account details section. Contact your brokerage's customer support if you are still looking for it online.
Alternatively, you can check the NSDL or CDSL websites. Depending on your DP, you will receive the letter from either the NSDL or the CDSL. An account number with 16 digits will appear on the letter you receive. In the case of CDSL letters, the Account number is also known as the Beneficiary Owner ID (BO ID).
Follow these steps to open an online demat and trading account:
- Visit the website of a reputable broker
- Complete the application form with your personal and financial details
- Upload required documents
- E-sign the application
- Wait for verification
- Start trading after receiving your account details.






