What Is a Put Option? - Meaning, Benefits, Working and More
Key Highlights
-
Put options give the holder the ability, but not the obligation, to sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price through a specified expiration date.
-
The premium is the upfront cost that the buyer of the option pays to the seller.
-
If the stock market is down, a put option can make you money, either as a short speculator or as a hedge against loss.
Put Option Meaning
In any market, there cannot be a buyer without there being a seller. Similarly, in the options market, you cannot have call options without having put options. Puts are options contracts that give you the right to sell the underlying stock at a pre-determined price on or before a specified expiry date in the future.
How Do Put Options Work?
In simple words,
- Traders buy puts when they expect the stock price to fall, allowing them to sell at a higher price than the market.
- If the stock’s price drops below the strike price, the buyer can sell at the agreed price and profit from the difference.
- If the stock stays above the strike price, the option may expire worthless, limiting the loss to the premium paid.
- Put options are often used to hedge against falling prices or to speculate on downward market moves.
Key Terms Related to Put Options
A put contract includes some basic terms that will help to better understand how it works:
Strike Price: A strike price is the predetermined future price at which you can buy a put option. Prior to entering into the contract, the buyer and seller agree on the strike price.
Spot Price: A spot price is the market price of the underlying asset.
Premium: The premium is the upfront fee the buyer pays to the seller. Option premiums are paid to the exchange and passed on to the seller.
Expiration: There's an expiration date on every put option. In other words, it's the future date of the contract's expiration or settlement. Put options can't be exercised after they expire.
Margins: Margin is leveraged to get the most from a put contract. It is possible to purchase a put option by paying an initial margin instead of the entire contract price.
Intrinsic and extrinsic value: A put option's value consists of intrinsic value (the difference between the strike price and spot price when favourable) and extrinsic value (time value and volatility).
Risk management: Put options are often used as a risk management tool, providing insurance against price declines while limiting losses to the premium paid.
Liquidity: The ease with which a put option can be bought or sold in the market affects its liquidity. High liquidity typically results in tighter bid-ask spreads, making transactions more cost-effective.
Volatility: Implied volatility significantly impacts the premium of a put option. Higher volatility increases the premium because the probability of the option ending in-the-money is greater.
Hedging: Investors use put options to hedge against potential losses in their portfolios. By holding put options, they can offset declines in the value of their assets.
Speculation: Traders also use put options to speculate on price declines. They can profit if the asset's price falls below the strike price before expiration.
Portfolio diversification: Including options in a portfolio can provide diversification benefits, as they behave differently from traditional equity investments.
Thus, using the above key terms to explain the workings of a put contract –
A buyer usually exercises a put option when the spot price is lower than the strike price. The difference between the strike price and spot price is the profit from the option. When a put option matures, it expires regardless of whether it is exercised.
A premium is a cost for an option buyer, so it reduces their gains. To buy a call and put option, most traders use margin. Also, trading on margin reduces capital employed dramatically.
Factors That Affect a Put's Price
Several factors influence a put option's price, including the underlying asset's current price, the strike price, time until expiration, volatility, and interest rates. These elements interact to determine the premium, which reflects the option's perceived value and risk.
Underlying asset price: The difference between the current market price and the strike price significantly impacts the option's intrinsic value. A larger gap in favour of the strike price increases the premium.
Time until expiration: Longer durations provide more opportunities for the market price to drop below the strike price, raising the option's time value and premium.
Volatility: Higher volatility suggests greater price fluctuations, increasing the likelihood of profitable scenarios for the option holder. As a result, volatile markets lead to higher premiums.
Interest rates: Changes in interest rates can affect the cost of carrying the underlying asset, indirectly influencing the option's price.

-
Fix the strike price (the amount at which you will buy in future)
-
Choose the expiry date
-
Select option price

-
Pay option premium to the broker
-
The broker transfers to exchange
-
Exchange sends the amount to option seller

-
Initial margin
-
Exposure margin
-
Premium margin/assignment margin

-
Stock call options
-
Index call options

-
Buyer of option pays you amount through brokers and the exchange
-
Helps reduce you loss or increase profit.
When to Buy a Put Option?
If, as an investor, you are concerned that the stock market will fall, you may buy put options. The reason is that a put will typically increase in value when the price of the underlying asset drops.
Having a put option can make you money in a down market, either as a short speculator or an investor hedged against losses. Therefore, whether you own stocks or simply wish to bet that the market will decline, you can benefit from buying put options
For speculators, put options offer a way to profit from anticipated market declines without owning the actual stocks. By purchasing puts, you can capitalise on downward price movements.
When to Sell a Put Option?
When you sell a put option, you promise to buy a stock at an agreed-upon price. It is better to sell put options only if you're comfortable owning the underlying security at the predetermined price, because you're assuming an obligation to buy if the counterparty exercises it.
When the stock price drops, sellers lose money. It's because they have to buy the stock at the strike price, but they can only sell it at a lower price. If the stock price rises, they profit since the buyer won't exercise.
Put sellers keep fees. They keep their businesses afloat by writing a ton of options on companies they think will appreciate. When stock prices fall, they think the fees they collect will cover the losses.
When to Hold or Exercise a Put Option?
Deciding whether to hold or exercise a put option depends on market conditions and your objectives as an investor. If the asset's price is approaching or has fallen below the strike price, exercising the option can lock in profits. Conversely, if the market price remains above the strike price, you may hold the option, hoping for a future decline. Careful analysis of market trends and potential catalysts is crucial in making this decision.
Is Buying a Put Similar to Short Selling?
While buying a put and short selling both aim to profit when a stock’s price falls, they operate quite differently. When you buy a put option, you gain the right to sell a stock at a predetermined price, limiting your maximum loss to the premium paid. In contrast, short selling involves borrowing shares and selling them in the market, with the hope of buying them back later at a lower price.
However, if the stock price rises instead of falling, losses can be unlimited in short selling. So, while both strategies share a similar objective, put options offer a built-in safety net, making them a more risk-controlled way to take advantage of a decline.
Benefits of Put Options
It is important to understand the benefits of buying a put vs. a call option when you buy an options contract. When compared to a call option, a put option has more advantages.
-
Profit potential in various market conditions
The underlying asset or stock can move in any direction. The value might fluctuate a lot depending on the economy, politics, and social events. A call option has to be purchased at a lower price than the strike price to be profitable for an investor.
By contrast, investors who buy put options might profit if the asset's price stays the same or even falls. Therefore, put option traders make more money than call option traders.
-
Advantage of time decay
To make money in derivatives trading, time is everything, and options are a time-bound asset that gives sellers an edge. The closer an option contract gets to its expiration date, the less valuable it becomes.
Because of this, put option sellers are more likely to profit from time decay if they sell while the option is still valuable. Those who have call options, on the other hand, aren't favoured by time decay.
-
Implied volatility advantage
An option contract's price tends to rise when implied volatility is high. For a put option trader, you want to sell when the price is high and buy when it's low. It's only conceivable when implied volatility is high but gradually declines.
It's long been known that high implied volatility tends to decline over time, so traders who buy put options would profit over time since the market's inherent conditions are in their favour.

Kinds Of Put Options:
There are two kinds of put options – American and European – on the basis of when an option can be exercised. American options are more flexible; they allow you to settle the trade before the expiry date of the contract. European options can only be exercised on the day of the expiry. Thus, index options are European options, while stock options are a kind of American options.

Illustration of a Put Index Option
Suppose the Nifty is currently trading at 6,000 levels. You feel bearish about the market and expect the Nifty to fall to around 5,900 levels within a month. To make the most of your view of the market, you could purchase a 1-month put option with a strike price of 5900. If the premium for this contract is ₹10 per unit, you will have to pay up ₹1,000 for the Nifty put option (100 units x ₹10 per unit).
So, if the index remains above your strike price of 5,900, you will not really benefit from selling at a lower level. For this reason, you would choose to not exercise your option. You just lose your premium of ₹1,000.
However, if the index falls below 5,900 levels as expected to say 5,850 levels, you are in a position to make profits from your options contract. You will thus choose to exercise your option and sell the index. That said, remember to take into consideration your premium costs. You will need to recover that cost too. For this reason, you will start making profits only once the index level falls below 5,890 levels.
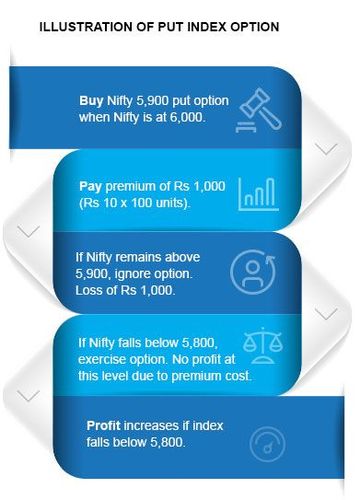
Illustration Of a Put Stock Option
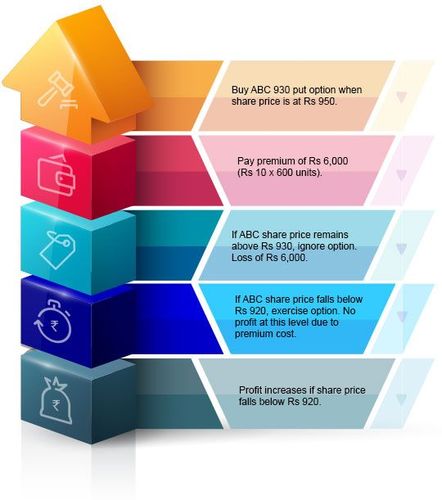
Suppose you hold ABC shares and you expect that its quarterly results are likely to underperform analyst forecasts. This could lead to a fall in the share prices from the current ₹950 per share.
To make the most of a fall in the price, you could buy a put option on ABC at the strike price of ₹930 at a market-determined premium of say ₹10 per share. Suppose the contract lot is 600 shares. This means, you have to pay a premium of ₹6,000 (600 shares x ₹10 per share) to purchase one put option on ABC.
Remember, stock options can be exercised before the expiry date. So, you need to monitor the stock movement carefully. It could happen that the stock does fall but gains back right before expiry. This would mean you lost the opportunity to make profits.
Suppose the stock falls to ₹930, you could think of exercising the put option. However, this does not cover your premium of ₹10/share. For this reason, you could wait until the share price falls to at least ₹920. If there is an indication that the share could fall further to ₹910 or 900 levels, wait until it does so. If not, jump at the opportunity and exercise the option right away. You would thus earn a profit of ₹10 per share once you have deducted the premium costs.
However, if the stock price actually rises and not falls as you had expected, you can ignore the option. Your loss would be limited to ₹10 per share or ₹6,000.
Thus, the maximum loss you face is the premium amount. The maximum profit is the share price minus the premium. This is because, shares, like indices, cannot have negative values.
Difference Between a Put Option And a Call Option
Even though call and put options do different things, they both make an options contract valid. For execution, they're both essential. Nevertheless, for a better understanding of the matter, let's draw a comparison table between call and put.
Call Option
In a call option, a person is given the right to purchase an underlying asset at a predetermined strike price and date, but not the duty to do so.
Put Option
In a put option, a person have the right, but not the obligation, to sell a certain quantity of an underlying asset at a certain price and date. In a contract, the strike price is the agreed-upon price.
Call Option
Call options payout if the underlying asset rises in value before the expiration date. The investor can effectively purchase the underlying asset for a much lower price than the market price if the value of the asset rises above the agreed-upon strike price.
Put Option
Put options are a great way for sellers to protect their investment if the price of the underlying asset drops in the future. It is possible that the value of the underlying asset will decline below what the buyer agreed to pay for it. Therefore, the buyer suffers a loss. However, since the contracting parties had already agreed to a strike price, even if the current price is lower, the seller will still receive the predetermined strike price.
| Call Option | Put Option |
|---|---|
In a call option, a person is given the right to purchase an underlying asset at a predetermined strike price and date, but not the duty to do so. | In a put option, a person have the right, but not the obligation, to sell a certain quantity of an underlying asset at a certain price and date. In a contract, the strike price is the agreed-upon price. |
Call options payout if the underlying asset rises in value before the expiration date. The investor can effectively purchase the underlying asset for a much lower price than the market price if the value of the asset rises above the agreed-upon strike price. | Put options are a great way for sellers to protect their investment if the price of the underlying asset drops in the future. It is possible that the value of the underlying asset will decline below what the buyer agreed to pay for it. Therefore, the buyer suffers a loss. However, since the contracting parties had already agreed to a strike price, even if the current price is lower, the seller will still receive the predetermined strike price. |
- | The seller benefits financially even if the asset's market value has plummeted. |
What Are Option Greeks?
Option Greeks are metrics that quantify the sensitivity of an option's price to various factors. Understanding these can aid investors in assessing risk and potential returns. The primary Greeks include the below.
Delta: Measures the option's price change relative to a change in the underlying asset's price.
Gamma: Indicates the rate of change of delta over time.
Theta: Represents time decay, reflecting the loss of value as the option approaches expiration.
Vega: Assesses sensitivity to changes in volatility.
Rho: Evaluates the impact of interest rate fluctuations.
Understanding Option Trading Strategies
Option trading strategies encompass a range of approaches that leverage the flexibility of options to achieve diverse investment goals. Some common strategies involving put options include the below.
Protective puts: Investors hold a long position in an asset and buy a put option to protect against downside risk. This combination acts as a safety net, ensuring that losses are limited if the asset's price declines.
Long puts: Investors purchase put options as a standalone strategy, anticipating a drop in the underlying asset's price. This approach offers high potential returns if the market moves as expected.
Bear put spreads: Involves buying a put option at a higher strike price and selling another at a lower strike price. This strategy reduces the net premium paid while maintaining the potential for profit if the asset's price decreases.
Straddles and strangles: These strategies involve buying both call and put options with the same expiration date but different strike prices. They are used when anticipating significant price movements in either direction, allowing investors to profit from volatility.
Conclusion
Put options are one of the many versatile tools available to investors like you for the management of risks and expectations of market declines. Understanding how put options work, the price determinants of a put option, and some of the strategies for trading them can help you find your way around financial markets with utmost confidence. Put options become especially strategic either in hedging or speculative operations for gaining an edge to reach any chosen investment objective.
FAQs on Put Options
A put option allows the holder to sell an asset at a specified price before a specified date.
An example would be to purchase a Rs. 100 put option on Stock X. The stock can be sold if its price falls below Rs. 100 before expiration.
A call option gives the holder the right to buy an asset at a specified price before a specified date.
An example would be to buy a call option on Stock Y with a strike price of Rs. 100. Prior to expiration, if the stock's price rises above Rs. 100, you can buy it at that price and sell it for a higher price.
CE is for "Call Option," and PE is "Put Option”.
Call options allow the holder to purchase the underlying asset, while Put options allow them to sell it.
Yes. A put is inherently less risky than a short.
Unless the contract is acted upon by the expiration date, it simply expires. The seller forfeits the premium you paid for the option. Nothing else needs to be paid.
No, you can’t exercise a put option before expiration.
You may be able to benefit from a sell put strategy if you know what you are doing, and it could also be used along with other strategies.
A put option is a financial contract giving the holder the right, but not obligation, to sell a specified amount of an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a set time.
Put options profit when the underlying asset's price decreases. They act as insurance, allowing the holder to sell at a predetermined price, regardless of market fluctuations.
Calls grant the right to buy an asset, while puts offer the right to sell. Both provide flexibility for investors to hedge or speculate on price movements.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. It is not produced by the desk of the Kotak Securities Research Team, nor is it a report published by the Kotak Securities Research Team. The information presented is compiled from several secondary sources available on the internet and may change over time. Investors should conduct their own research and consult with financial professionals before making any investment decisions. Read the full disclaimer here.
Investments in securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. Brokerage will not exceed SEBI prescribed limit. The securities are quoted as an example and not as a recommendation. SEBI Registration No-INZ000200137 Member Id NSE-08081; BSE-673; MSE-1024, MCX-56285, NCDEX-1262.






